The Circular Flow of
What is the Circular Flow Model? The circular flow model is an economic model that presents how money, goods, and services move between sectors in an economic system. The flows of money between the sectors are also tracked to measure a country's national income or GDP, so the model is also known as the circular flow of income. Summary
The Circular Flow of Intelligent Economist
The Circular Flow of Income is the economic concept of the constant flow of money. It shows the interdependence of different economic sectors. In addition, it highlights the link between earning and spending in an economy. Thus, it becomes vital to understand the income flow to understand the economic wealth of a nation.

Circular Flow of Circular flow of Finance blog, Finance
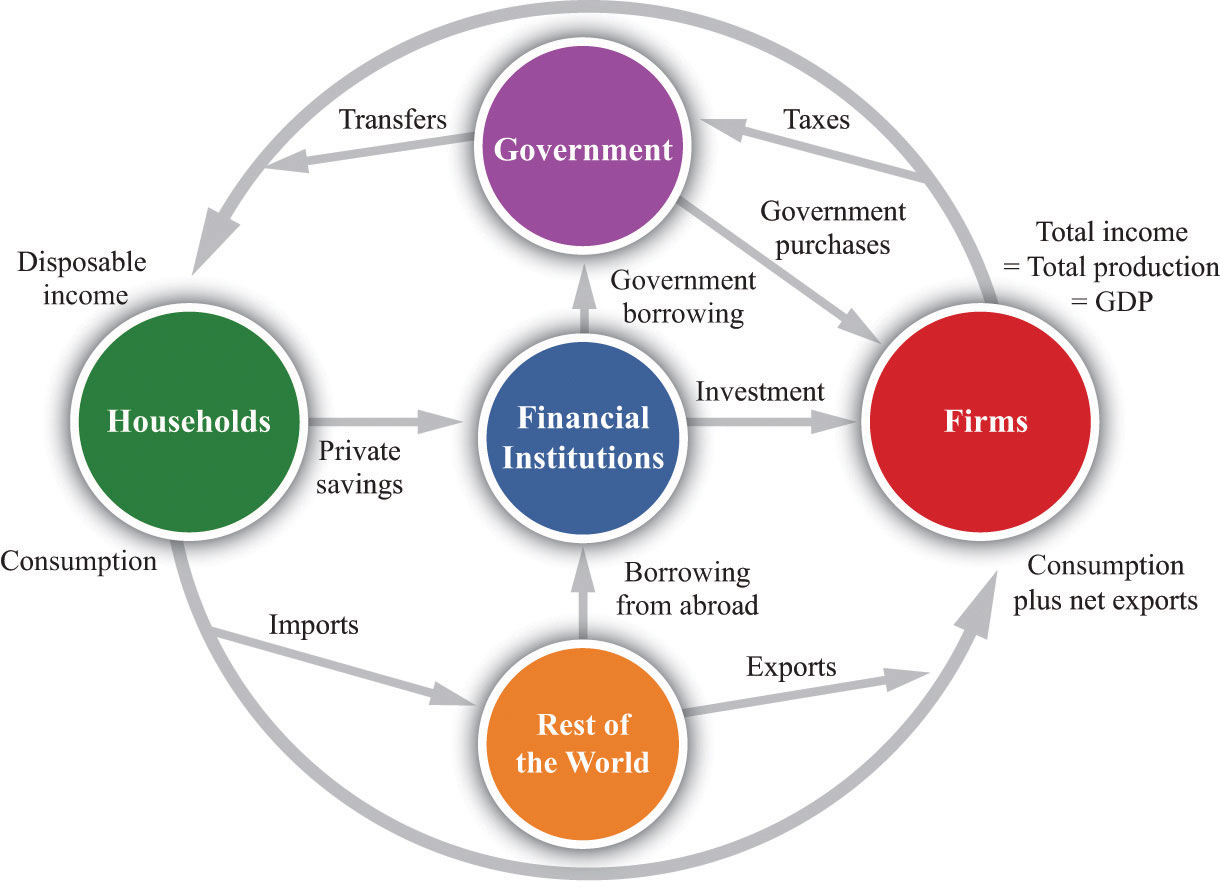
The circular flow diagram illustrates the equivalence of the income approach and expenditures approach to calculating national income. In this diagram, goods, services, and resources move clockwise, and money (income from the sale of the goods, services, and resources) moves counterclockwise.
Schmidtomics An Economics Blog Circular Flow of
From a simple version of the circular flow, we learn that—as a matter of accounting—. gross domestic product(GDP) = income = production = spending. (31.28.1) (31.28.1) g r o s s d o m e s t i c p r o d u c t ( G D P) = i n c o m e = p r o d u c t i o n = s p e n d i n g. This relationship lies at the heart of macroeconomic analysis.
What are the main features of the five sector circular flow model? How is equilibrium achieved
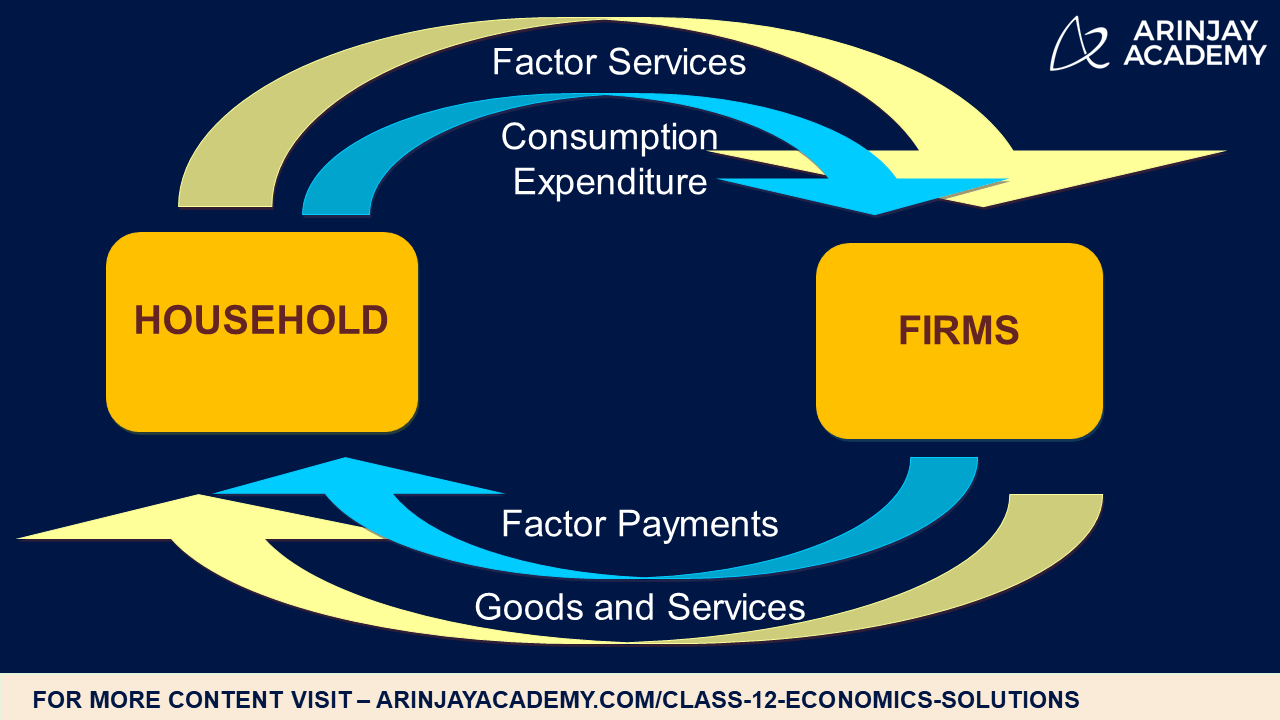
The Circular flow of income diagram models what happens in a very basic economy. In the very basic model, we have two principal components of the economy: Firms. Companies who pay wages to workers and produce output. Households. Individuals who consume goods and receive wages from firms.

Circular Flow of and ExpenditureFour Sector Economy Businesstopia
A circular flow of goods and services result from factors of production and goods and services received. GDP can be measured as total expenditures, total income, or total revenue. Created by Sal Khan. Questions Tips & Thanks Want to join the conversation? Sort by: Top Voted Manu 10 years ago How is he profiting from his payment?

Circular flow of model explanation & example Management Gurus Call TheONE
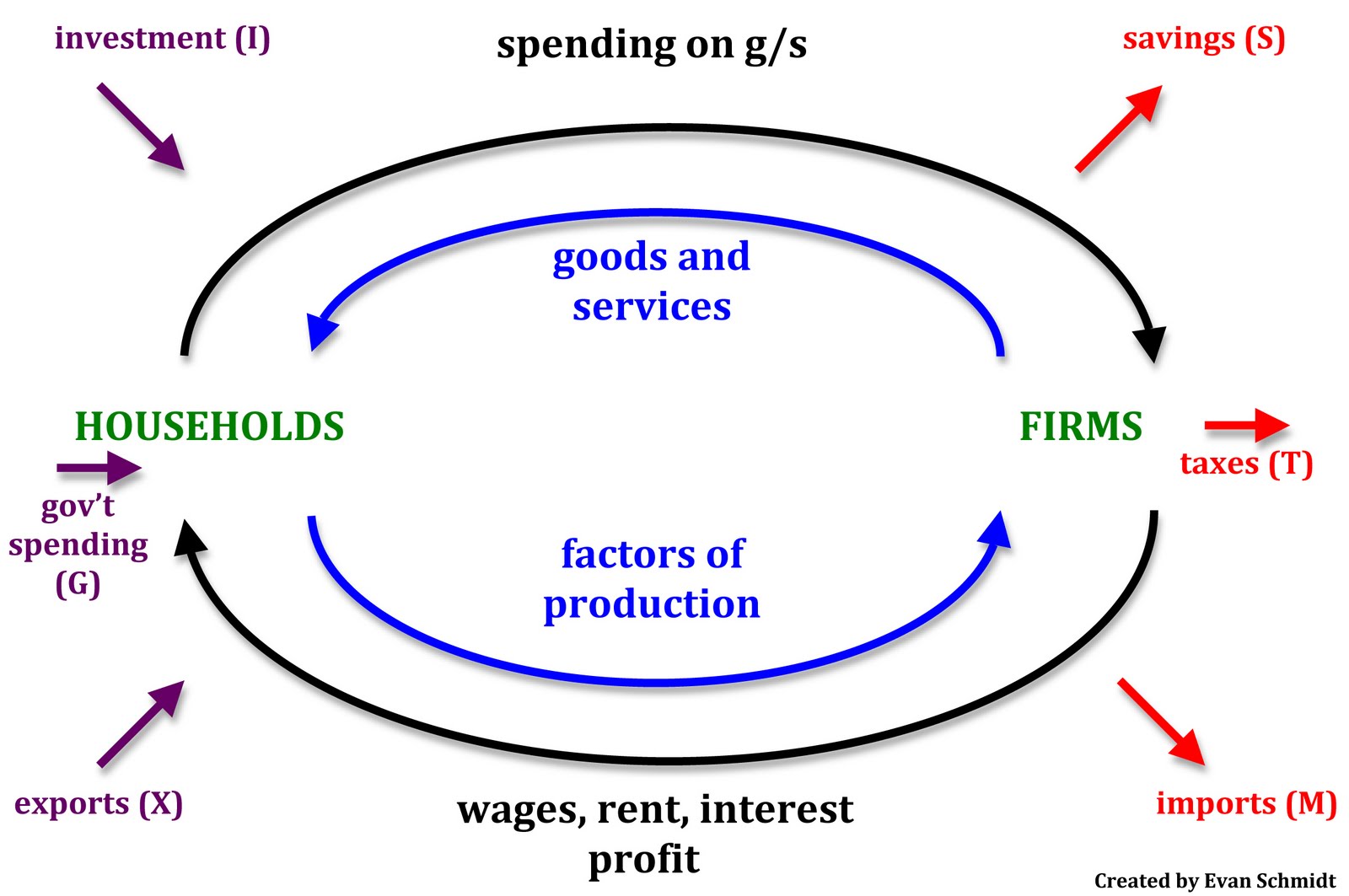
The circular flow of income or circular flow is a model of the economy in which the major exchanges are represented as flows of money, goods and services, etc. between economic agents. The flows of money and goods exchanged in a closed circuit correspond in value, but run in the opposite direction.
Explain Circular flow of in two sector economy Arinjay Academy
From a simple version of the circular flow, we learn that, as a matter of accounting, gross domestic product (GDP) = income = production = spending. (18.4.1) (18.4.1) g r o s s d o m e s t i c p r o d u c t ( G D P) = i n c o m e = p r o d u c t i o n = s p e n d i n g. This relationship lies at the heart of macroeconomic analysis.

Circular flow of in Two Sector economy Economics Class 12 Macroeconomics YouTube
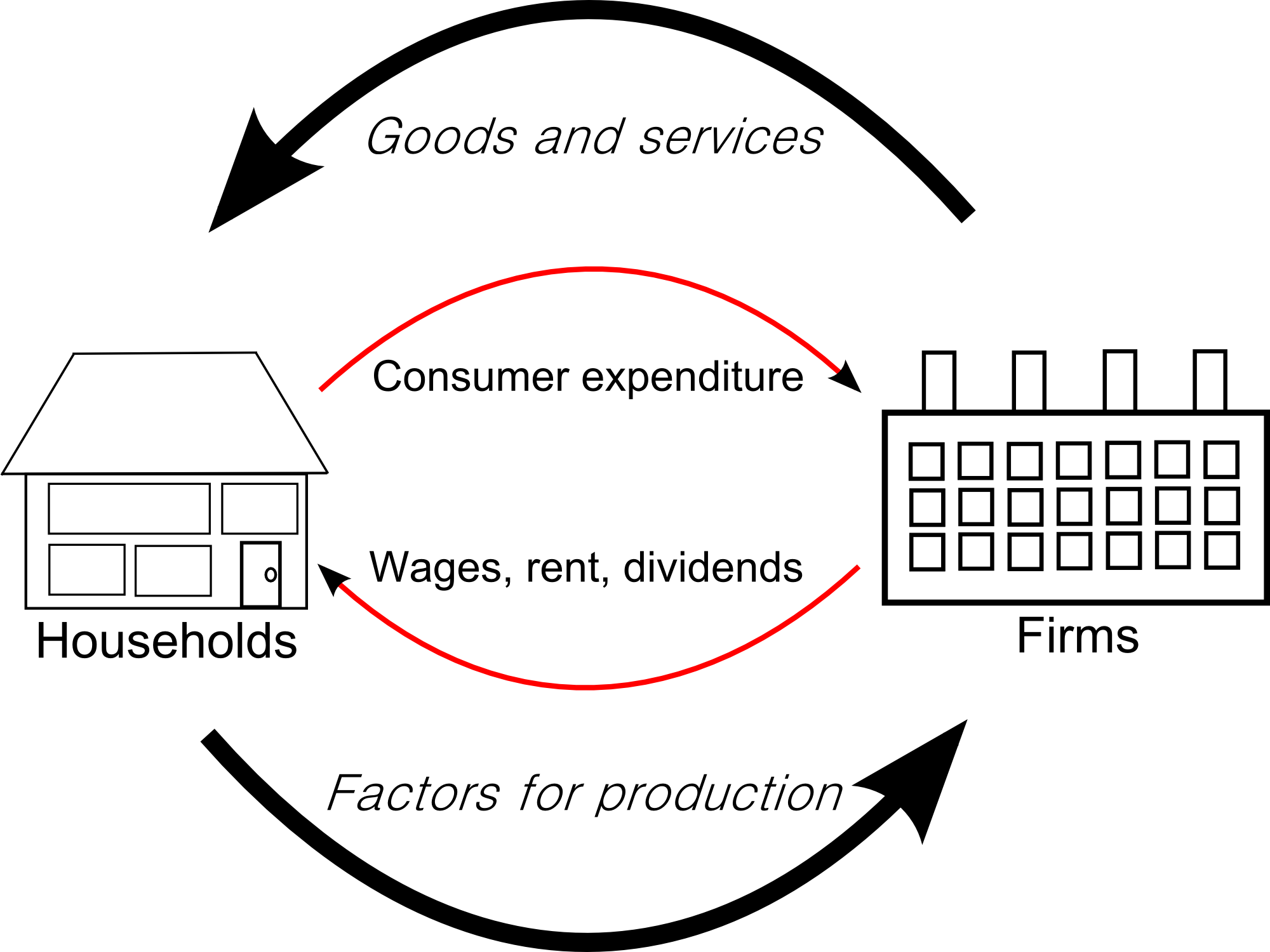
Circular Flow of Income Basic Concept of the Circular Flow of Income. The Circular Flow of Income represents the flows of money and goods exchanged within an economy. It's a model that helps depict how money and goods move through an economy. There are typically two main agents in the model: households and firms. The Role of Households and.

Understanding the Circular Flow of and… tutor2u Economics
The circular flow model is a simplified representation of how money flows within an economy, illustrating the redistribution of income. It is crucial for calculating national income and is a key concept in macroeconomics. Circular flow models help in analyzing economic equilibrium, demonstrating the impact of government involvement and trade.
5 Sector Circular Flow Model
The circular flow of income demonstrates how economists calculate national income, or gross domestic product (GDP). Contents show The Dual Categories for Economic Actors, Markets, and Cycles Within this model, all economic actors are placed into one of two categories: households or companies (firms).
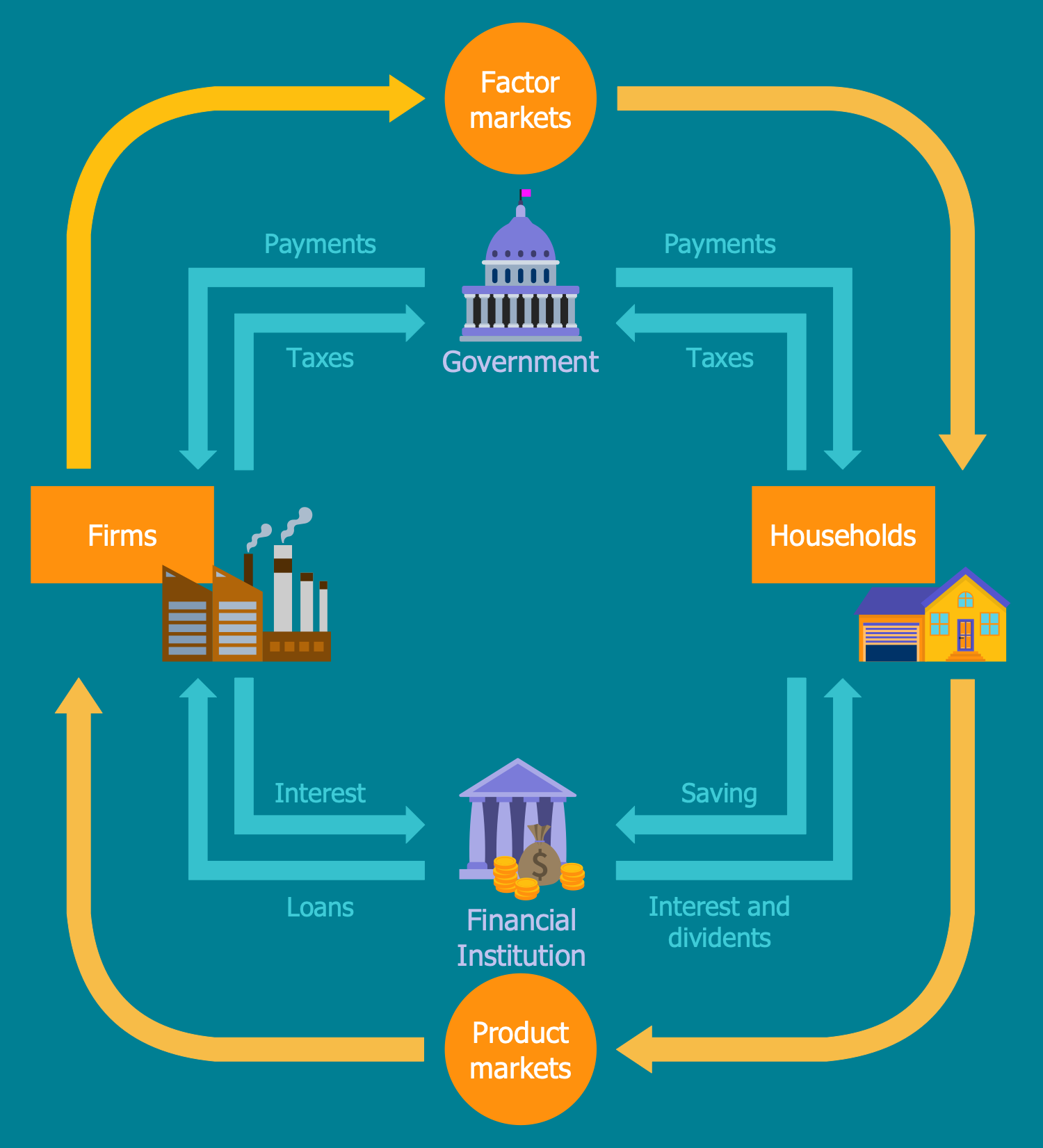
5 Sector Circular Flow Model
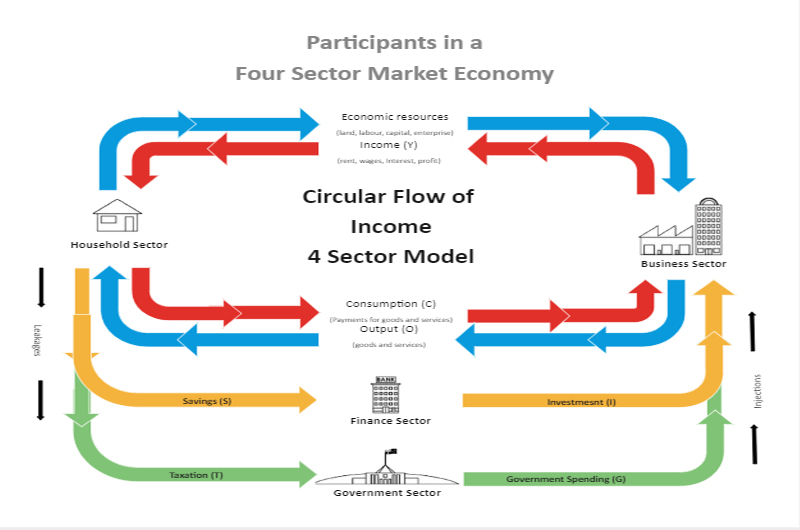
The only difference in the circular flow of income between a closed economy and an open economy is that, in a four-sector economy, households purchase foreign-made goods and services (i.e., imports). Likewise, people of other countries purchase goods and services not produced domestically (i.e., exports).

Circular Flow Diagram definition and examples (2022)
The circular flow of income model is a simplified representation of the flow of money, goods, and services between households and firms in an economy. In the News Teaching Activity - BoE warns against early interest rate cut (Nov 2023) 2.4.1 Circular Flow Model (Edexcel A-Level Economics Teaching PowerPoint)

Understanding the Circular Flow of and… tutor2u Economics
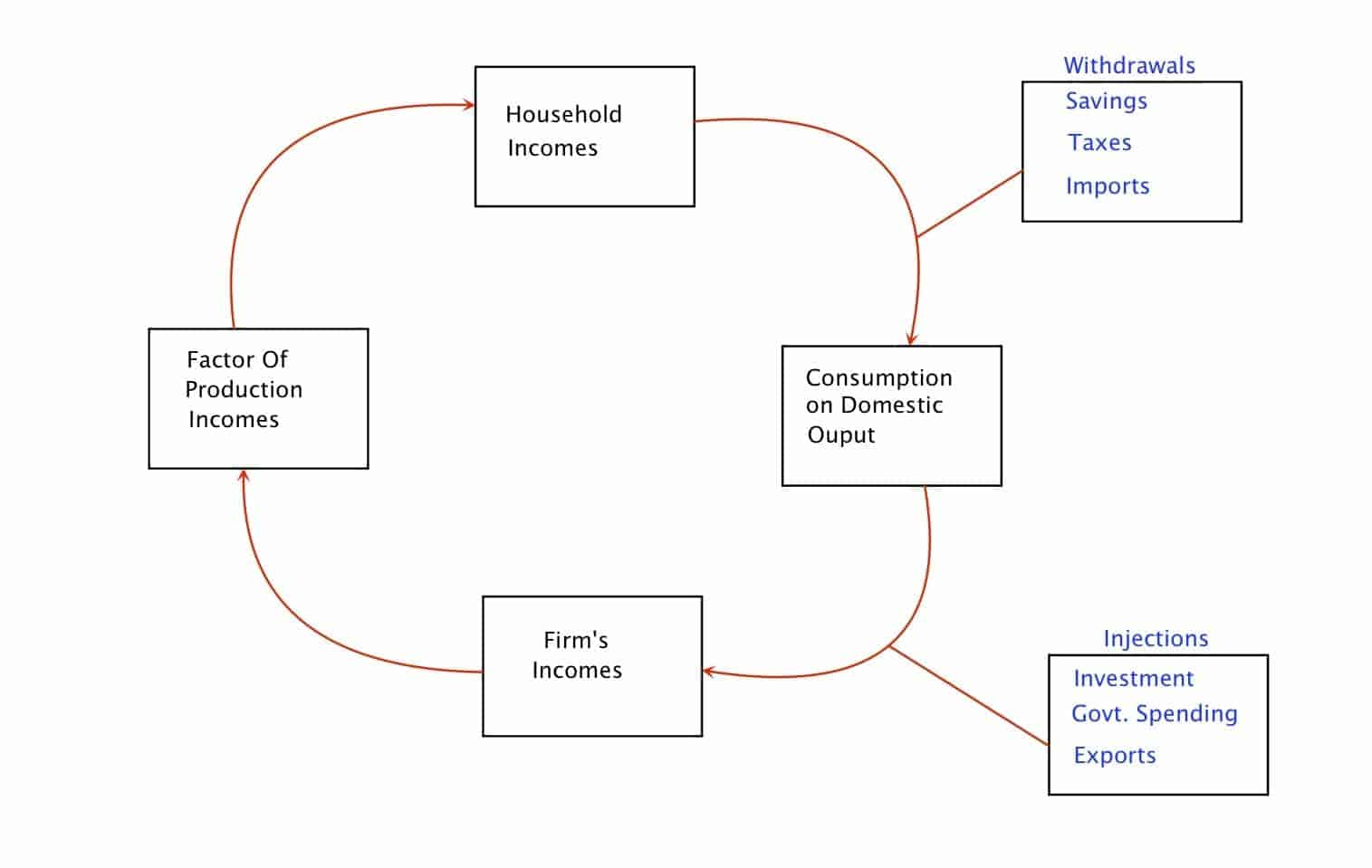
The Circular flow of income Income (Y) in an economy flows from one part to another whenever a transaction takes place. New spending (C) generates new income (Y), which generates further new spending (C), and further new income (Y), and so on.

The Circular Flow of
In short, an economy is an endless circular flow of money. That is the basic form of the model, but actual money flows are more complicated. Economists have added in more factors to better.

What is Circular Flow of definition, economic sectors, types, phases, twosector, three
The economy can be thought of as two cycles moving in opposite directions. In one direction, we see goods and services flowing from individuals to businesses and back again. This represents the idea that, as laborers, we go to work to make things or provide services that people want. In the opposite direction, we see money flowing from businesses to households and back again.